Continuously curved river
Let's take a look!
What type of experiment is this?
Experimental procedure and explanation:
- Let’s conduct an experiment to determine how a continuous winding river flows and how deposition occurs.
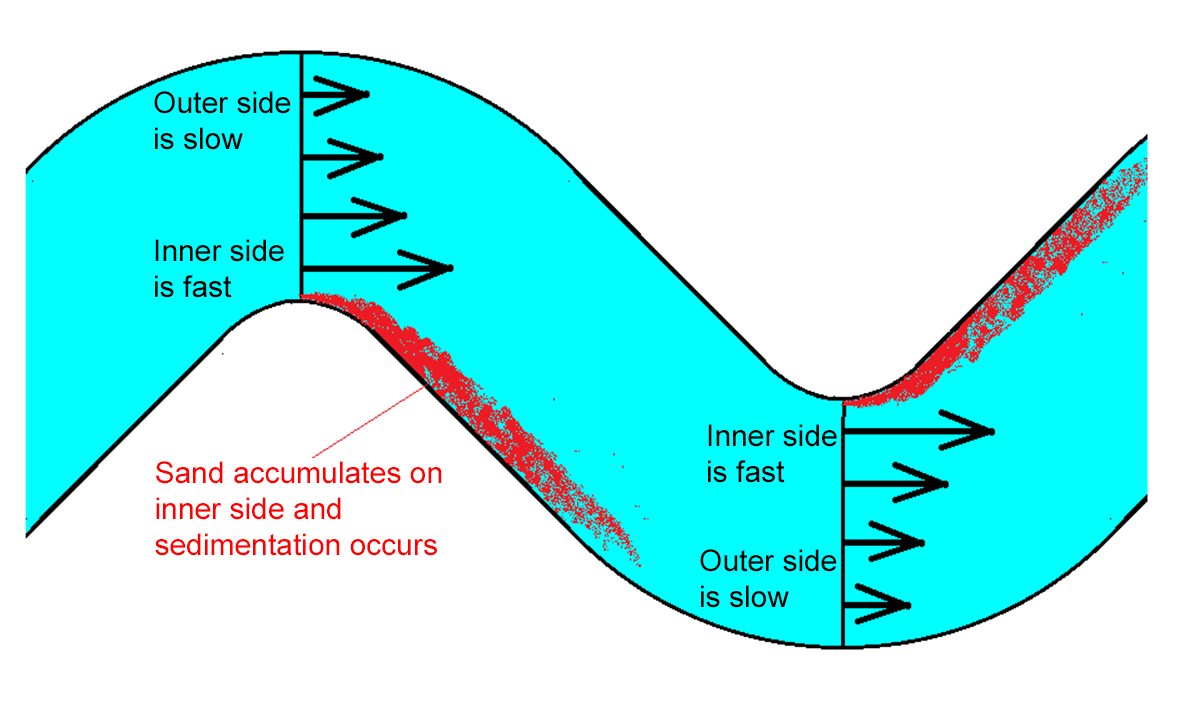
- If shredded paper is floated on the water surface, it can be observed that the paper flows slowly on the outer side and faster on the inner side in the curve. We can also observe that it moves to the outer side.
- Next, a soaked paper is submerged into the water, you can see that it moves to the inner side near the river bed and gets deposited there. This is the same as in “Secondary flow and sediment in curved river”. (what looks like glittering light once the paper is submerged is caused by ripples on the water surface, and it is unrelated to the movement of the paper.)
- Regardless of whether the flow is faster on the outer or inner side, a secondary flow occurs in a curved river, causing sediment to accumulate on the inner side. Hence, sand and dirt often accumulate on the inner side of curves in actual rivers. However, due to the effect of gravity, larger stones tend to sink and deposit in deeper areas,
- This video of the experiment was produced with the support of JSPS KAKENHI 18K03956.
| [Keywords] | Curved river |
| [Related items] | Speed of flow in a curved river 2, Secondary flow and sediment in curved river |
| [Reference] | “The Wonders of Flow,” Japan Society of Mechanical Engineering, Kodansha Blue Backs, p. 60–61. |
Last Update:2.6.2024

