Newsletter 2021.1 Index
Theme : "Mechanical Engineering Congress, 2020 Japan (MECJ-20)”
|
Modeling of a Two-Phase Flow Simulation with the Evaporation of the Gas Diffusion Layer in a Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Ryuya NAGAYAMA Ibaraki University |
Satoshi SAKAIDA Ibaraki University |
Kotaro TANAKA Ibaraki University |
Mitsuru KONNO Ibaraki University |
Abstract
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) are clean power sources that generate electric energy by the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. Because the PEFC has good characteristics such as high efficiency, harmless emissions, and quick start up, the PEFC has attractive attention as the next generation power source for vehicles. However, to make the PEFC commercially competitive in the market, it is an important issue to achieve the high current density operation. For the high current density operation, the optimization of the water transport with phase change in the cell with complicated structure is necessary. In this study, the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) which can simulate the water and vapor transport in the cell was developed. We used a free energy-based LBM for two-phase flow with a large density ratio, and the source term for phase change was added to the Cahn-Hilliard equation in this LBM model. In addition, the convection-diffusion equation was also added to simulate the vapor transport. To verify the developed LBM model, the water flow with evaporation in a two-dimensional porous media similar with the gas diffusion layer in the PEFC was investigated. The experiment was carried out in the thermostatic chamber set at 70℃ which is the typical operating temperature in the PEFC. The simulation result of water behavior in the porous medium showed the good agreement with the experimental result. This result suggests that the developed model can simulate the water transport with evaporation in the gas diffusion layer of the PEFC.
Key words
Lattice Boltzmann Method, Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell, Two-Phase Simulation, Evaporation
Figures
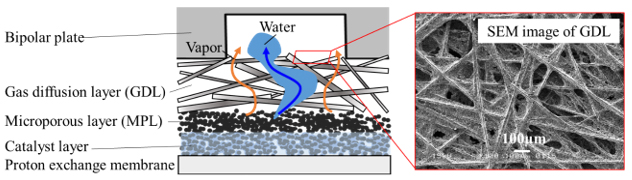
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of polymer electrolyte fuel cell.
 |
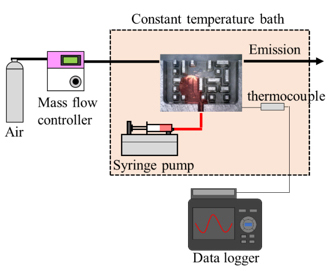 |
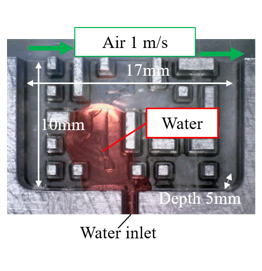
| (a) Porous area imitating GDL | (b) Overall view of the experimental equipment |
| Fig.2 Porous area imitating GDL. | |
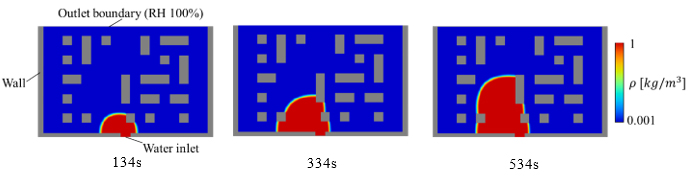
(a) Simulation
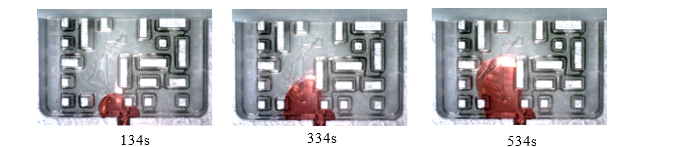
(b) Experiment
Fig.3 Comparison of water flow in a two-dimensional porous structure
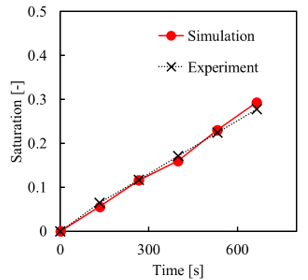
Fig.4 Saturation of complex water flow in porous area

